FAA’s ROADMAP for the unknowable AI future

The FAA has issued “A ROADMAP for ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE SAFETY ASSURANCE”, 31 pages of necessarily GENERAL guidance for industry to refer to while our industry traverses this change at warp speed. The roadmap attempts to set major principles to define what the regulators may require for designs and operations that are as-of-yet unknowable. AI has been a source of many posts here recently; here is a sample of them:
- ATC and AI—an expert opines.
- EASA offers insights where AI is going in aviation.
- AI comments on EASA’s 2nd issue paper on Artificial Intelligence
- FAA RFI for AI integration of Safety Data Sources with Predictive tools

ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE, to steal an apt phrase coined by Winston Churchill, is “a riddle wrapped in a mystery inside an enigma.” [For those who are unsure exactly what AI is, can be or should not be, The Alignment Problem: Machine Learning and Human Values, by Brian Christian, has helped explain from whence it came and some of the places AI may go.] The National Academies recently warned that aviation innovation will test the FAA’s ability to meet its mission during this period of dynamic change.
Attached is a trade publication review of the FAA’s paper. Below is a set of abbreviated excerpts to whet your appetite for reading all of the guidance:

p.3
“Artificial Intelligence (AI) has generated significant interest in aviation, from offline applications to process control to on-aircraft autonomy. Prior to its utilization in aviation, this technology must demonstrate its safety. However, it presents a NEW CHALLENGE FOR SYSTEMS that ACHIEVE PERFORMANCE AND CAPABILITY BY LEARNING RATHER THAN DESIGN due to the absence of engineering principles that guide the traditional engineering design process.
The document introduces a set of principles (valued concepts that are independent of time, resources, and situation) to guide the development of methods for the safety assurance of AI in aircraft and aircraft operations, including:
• Work Within the Aviation Ecosystem: Use existing aviation safety requirements. Introduce AI within this structured, disciplined, and risk-managed ecosystem.
- Principle: Use existing civil aviation safety requirements, processes, and methods to introduce AI, except where they are found to be inadequate.
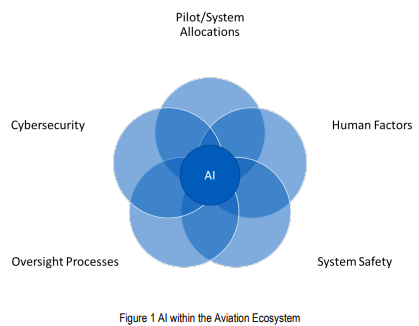
• Focus on Safety Assurance and Safety Enhancements: Center AI development in aviation on safety of AI and using AI for safety, targeting improvements in safety, and ensuring ethical considerations, particularly those that may affect safety, are addressed.
- Principle: ADDRESS SAFETY WITHIN THE REGULATORY FRAMEWORK.
• Avoid Personification: TREAT AI AS A TOOL, NOT A HUMAN. Emphasize clear responsibility assignment and avoid human-centric language to maintain a clear understanding of AI’s role and limitations in aviation.
- Principle: TREAT AI AS AN ALGORITHM OR COMPUTER, NOT AS A HUMAN
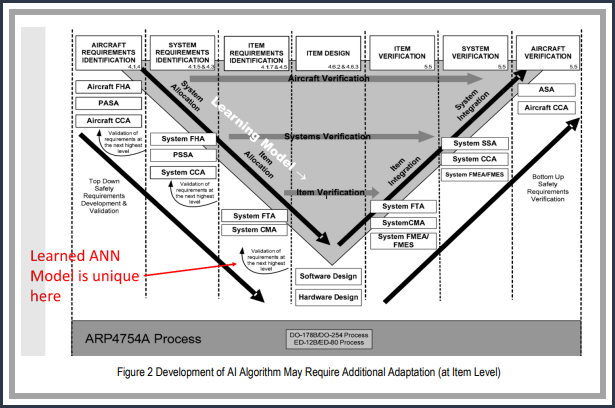
• Differentiate between Learned and Learning AI2: Establish distinct safety assurance methodologies for learned (static) AI and learning (dynamic) AI, understanding the difference their respective operational and safety implications.
- Principle: Distinguish between the safety assurance methodology for learned AI implementations and learning AI implementations. A key characteristic of AI in the context of safety assurance is that AI systems often gain significant capabilities through learning processes, in addition to what is explicitly programmed or designed. The use of AI CAN BE FURTHER DIVIDED BETWEEN IMPLEMENTATIONS OF FIXED AND DETERMINISTIC ALGORITHMS, AND IMPLEMENTATIONS THAT CONTINUE TO CHANGE THROUGH LEARNING IN THE OPERATIONAL ENVIRONMENT
- LearnED AI Implementation: AI implementations that are static in the operating environment. These implementations encompass Machine Learning (ML) algorithms that are developed through offline training, and the specific learned AI is subjected to design time safety assurance processes prior to its use in an operational context.
- LearnING AI Implementation: AI implementations that are dynamic in the operating environment. These implementations involve the incorporation of learning mechanisms into the AI system itself, so it is not possible to qualify each version: instead, the safety assurance strategy will need to address the learning itself.
• Take an Incremental Approach: Implement AI in aviation incrementally, learning and adapting safety assurance methods based on real-world application and experience.
- Principle: Adopt an incremental approach to the introduction of AI in aviation safety assurance, updating with experience.
• Leverage the Safety Continuum: Utilize the safety continuum, starting with lower-risk applications to gain experience and inform broader applications and safety methods.
- Principle: Gain experience in lower-risk applications
p.4
• Leverage Industry Consensus Standards: Adopt industry consensus standards for AI safety assurance in aviation, as appropriate, promoting global harmonization and adapting to technological changes while aligning with the principles in the roadmap.
- Principle: Use industry consensus standards that provide acceptable means of compliance for aviation safety assurance, as appropriate.
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
This roadmap identifies next steps in five areas to enable safety enhancements and the safe use of AI:
• Collaboration: Establish ongoing partnerships with industry, government, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), and other appropriate domestic and international stakeholders to share insights and develop harmonized global AI safety assurance methods, as appropriate.
• FAA Workforce Readiness: ENHANCE KNOWLEDGE AND EXPERIENCE IN THE FEDERAL AVIATION ADMINISTRATION (FAA) WORKFORCE TO EFFECTIVELY OVERSEE THE DESIGN AND INTEGRATION OF AI TECHNOLOGIES IN AVIATION.
• Assure the Safety of AI: Adapt and develop safety assurance methods specifically for AI, utilizing conventional frameworks and developing new approaches tailored to AI’s unique challenges. Ensure any AI system put into an aircraft is safe.
• Use AI for Safety: Leverage AI to improve the fidelity and effectiveness of safety lifecycle processes, from monitoring to system development and testing.
• Aviation Safety Research: Conduct focused research to develop and evaluate methods for assuring the safety of AI systems and using AI to enhance overall aviation safety. This is a living document that the FAA plans to update periodically to both reflect progress in safety assurance and adapt to rapidly evolving AI technology.
The document is alive with expectations that as unexpected developments occur, the FAA will modify the principles and/or applications.

FAA Unveils AI Integration Aviation Roadmap as States Eye Regulations
By PYMNTS | August 28, 2024
|

FAA Charts Course for AI Integration in Aviation
The FAA has unveiled its initial “Roadmap for Artificial Intelligence Safety Assurance,” a 31-page document outlining its strategy for safely incorporating artificial intelligence technologies into the aviation sector.
The roadmap establishes guiding principles for AI safety assurance in aircraft and aircraft operations. It emphasizes working within the existing aviation ecosystem, focusing on safety enhancements and taking an incremental approach to AI integration.
“The recent acceleration in the development of artificial intelligence provides new opportunities to leverage the technology to support a safe aviation system, while posing new risks if not appropriately qualified and used,” David H. Boulter, FAA Associate Administrator for Aviation Safety, wrote in the document. “In the face of these challenges and opportunities, we have developed this roadmap to explain our approach to developing methods to assure the safety of the technology and introduce it for safety.”
“It lays out a strategy to pursue both the safety of AI and the use of AI for safety,” he added.
The document identifies five critical areas for enabling safe AI use: COLLABORATION, FAA WORKFORCE READINESS, ASSURING AI SAFETY, LEVERAGING AI FOR SAFETY IMPROVEMENTS AND AVIATION SAFETY RESEARCH.
The FAA plans to collaborate with industry, other government agencies and international partners to develop harmonized global AI safety assurance methods. The agency will also enhance its workforce’s AI knowledge and adapt existing safety assurance methods for AI systems.
The FAA said it plans to update the roadmap periodically to reflect progress in safety assurance and adapt to rapidly evolving AI technology.
